A System For The Continuous Directed Evolution Of Biomolecules
A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules. Ad Directed Molecular Evolution Services. Ad Directed Molecular Evolution Services. A system for the continuous directed evolution of biomolecules Researchers in the laboratory of Professor David Liu have developed a platform that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in E.
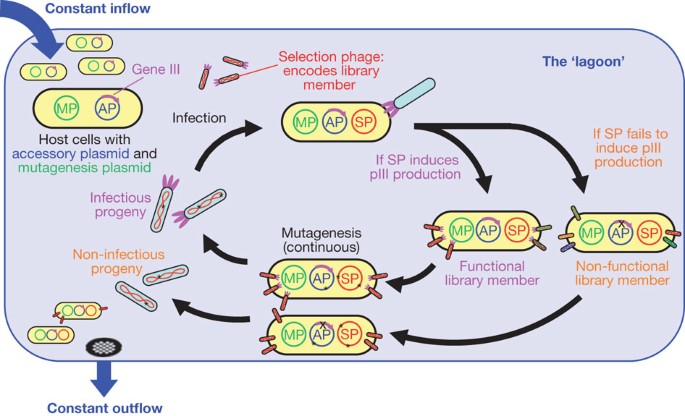
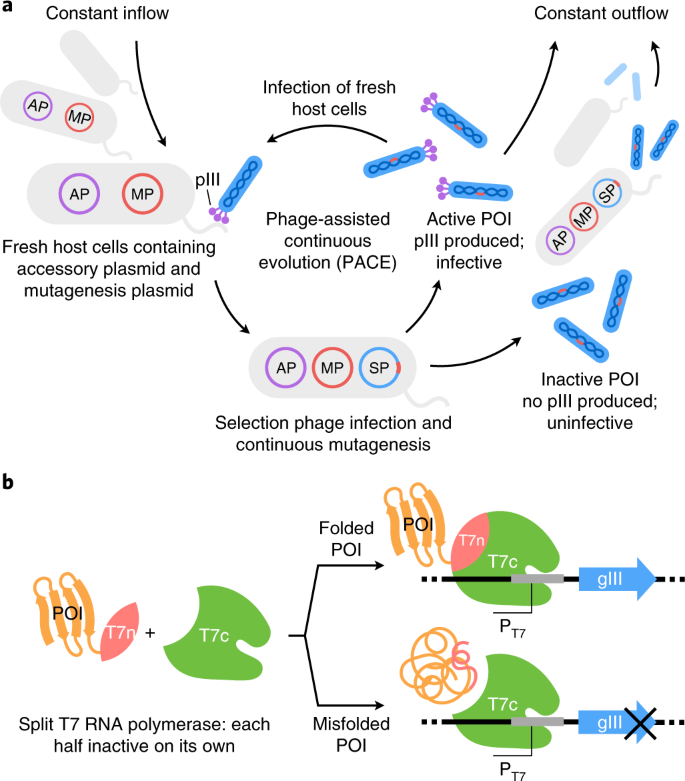
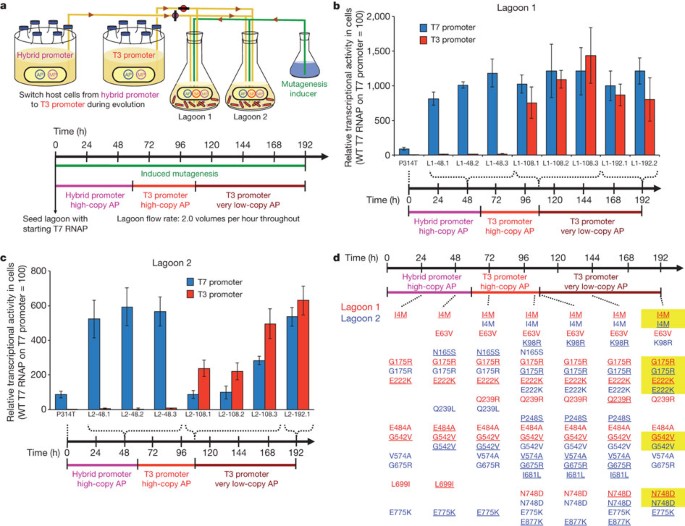
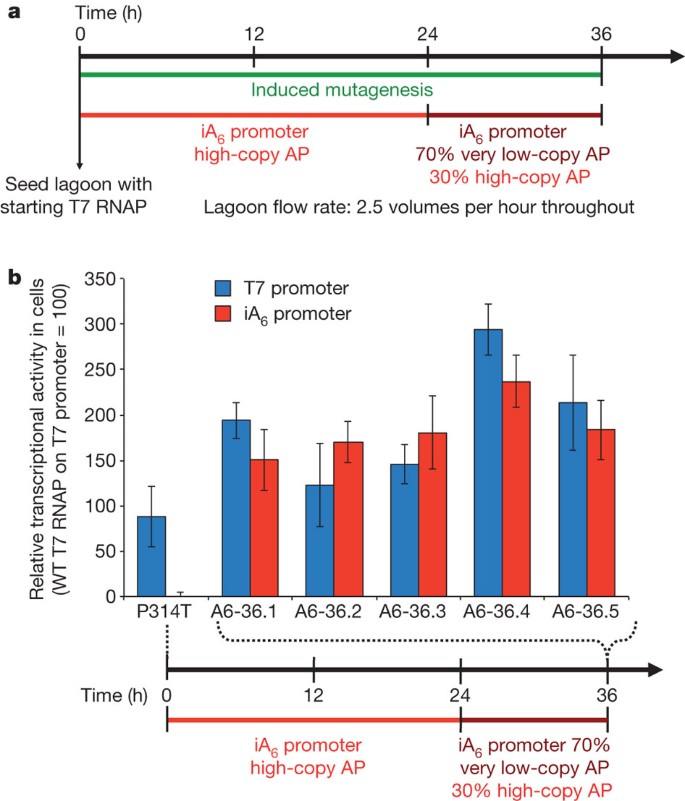
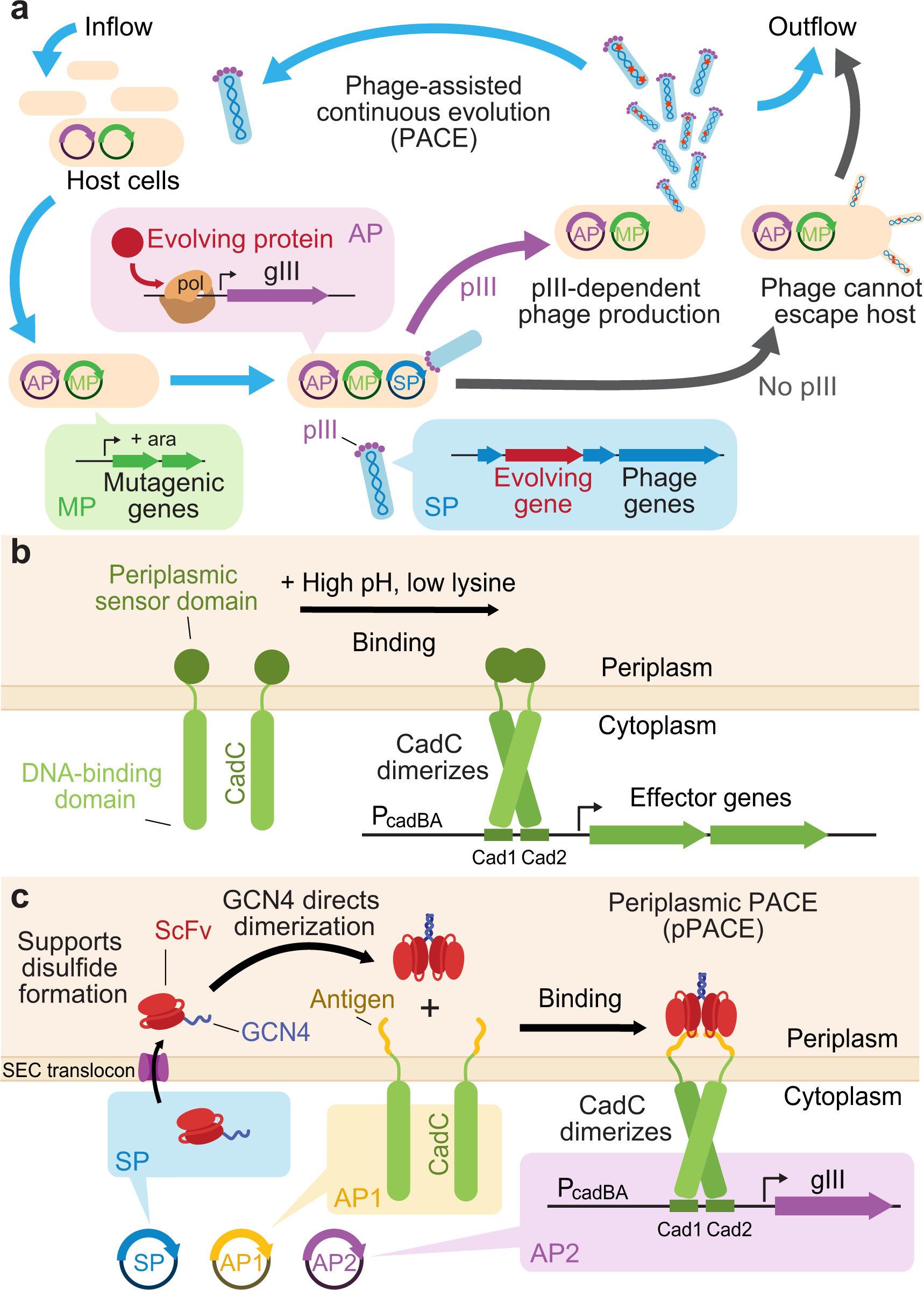
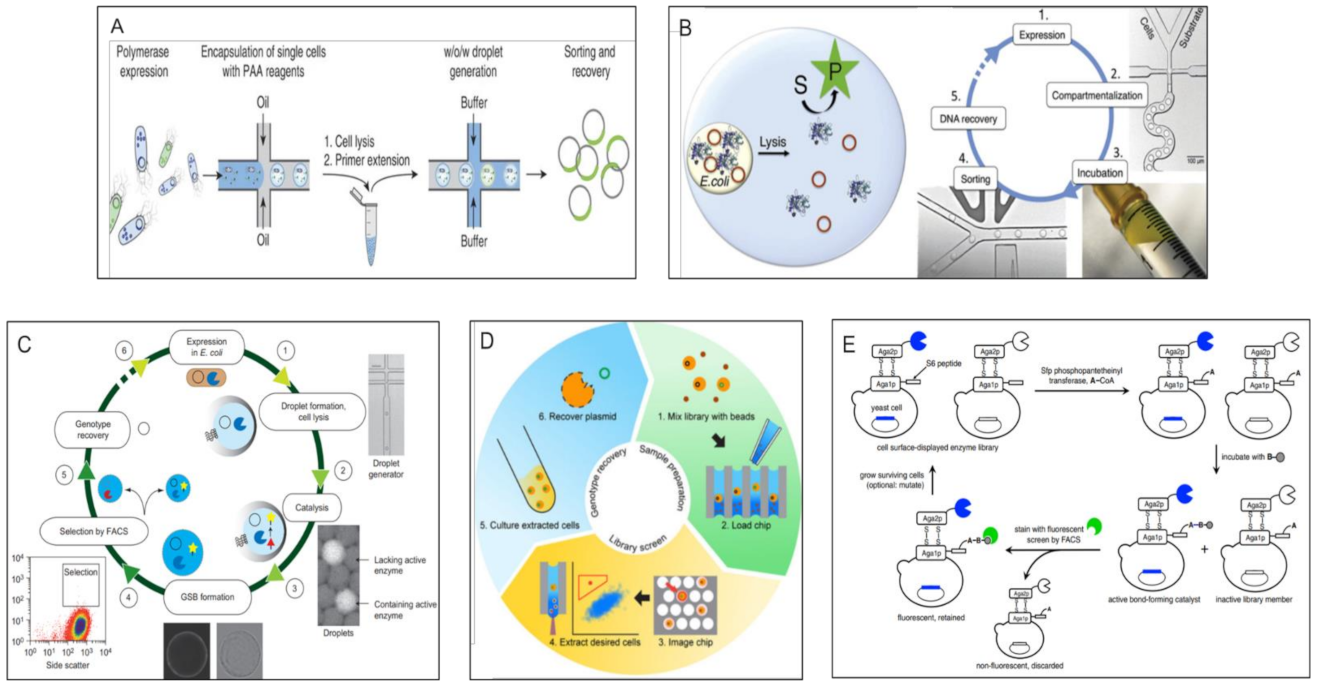
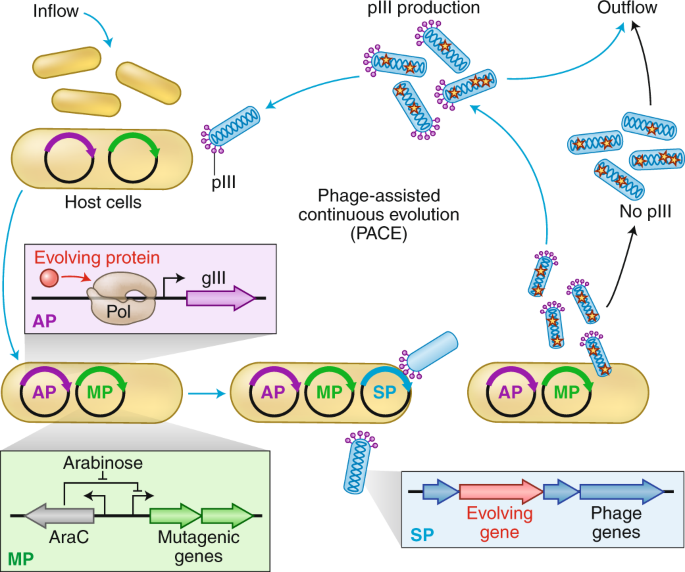
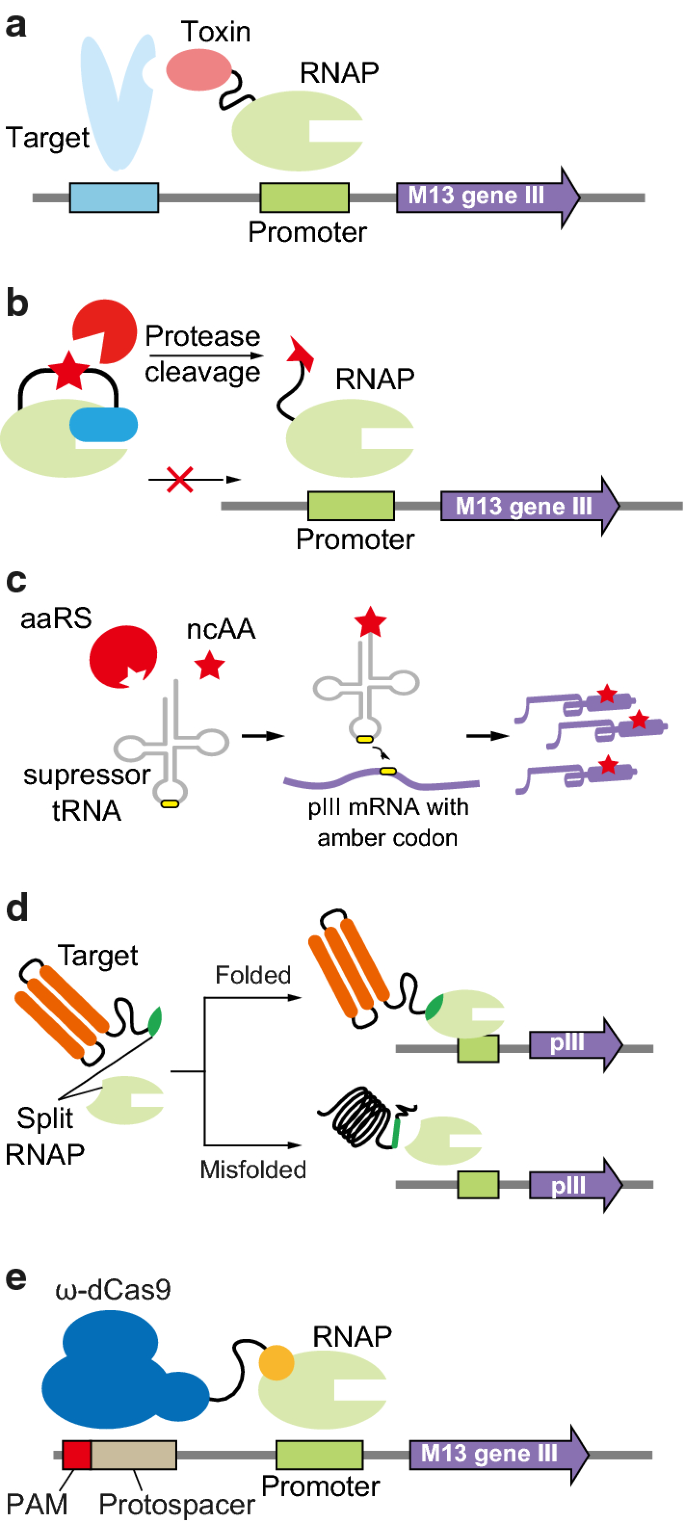
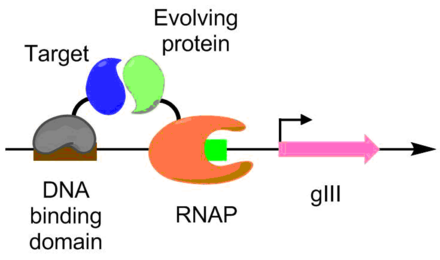
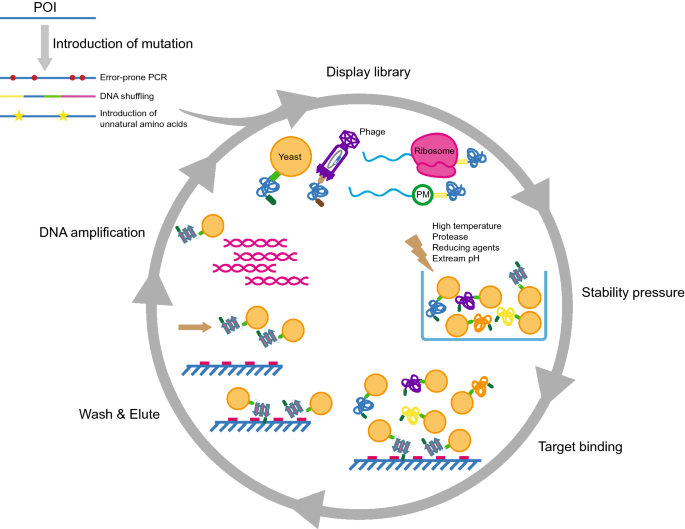
During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of interest. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of interest. Here we describe periplasmic phage-assisted continuous evolution pPACE a system for continuous evolution of protein-protein interactions in.
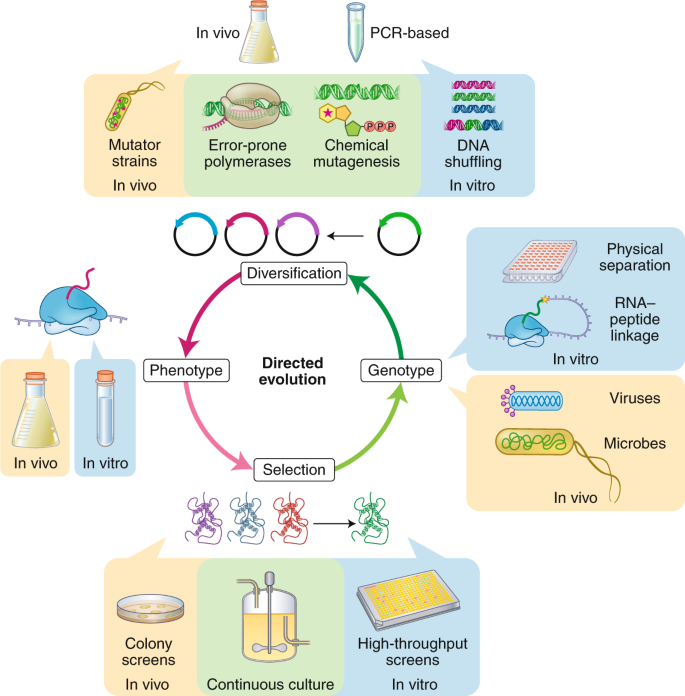
Continuous directed evolution methods allow the key steps of evolutiongene diversification selection and replicationto proceed in. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of.
Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli. Now describe a phage-assisted continuous evolution system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli.
Liu journalNature year2011 volume472 pages499 - 503. A System for the Continuous Directed Evolution of Biomolecules articleEsvelt2011ASF titleA System for the Continuous Directed Evolution of Biomolecules authorK. Now describe a phage-assisted continuous evolution system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be.
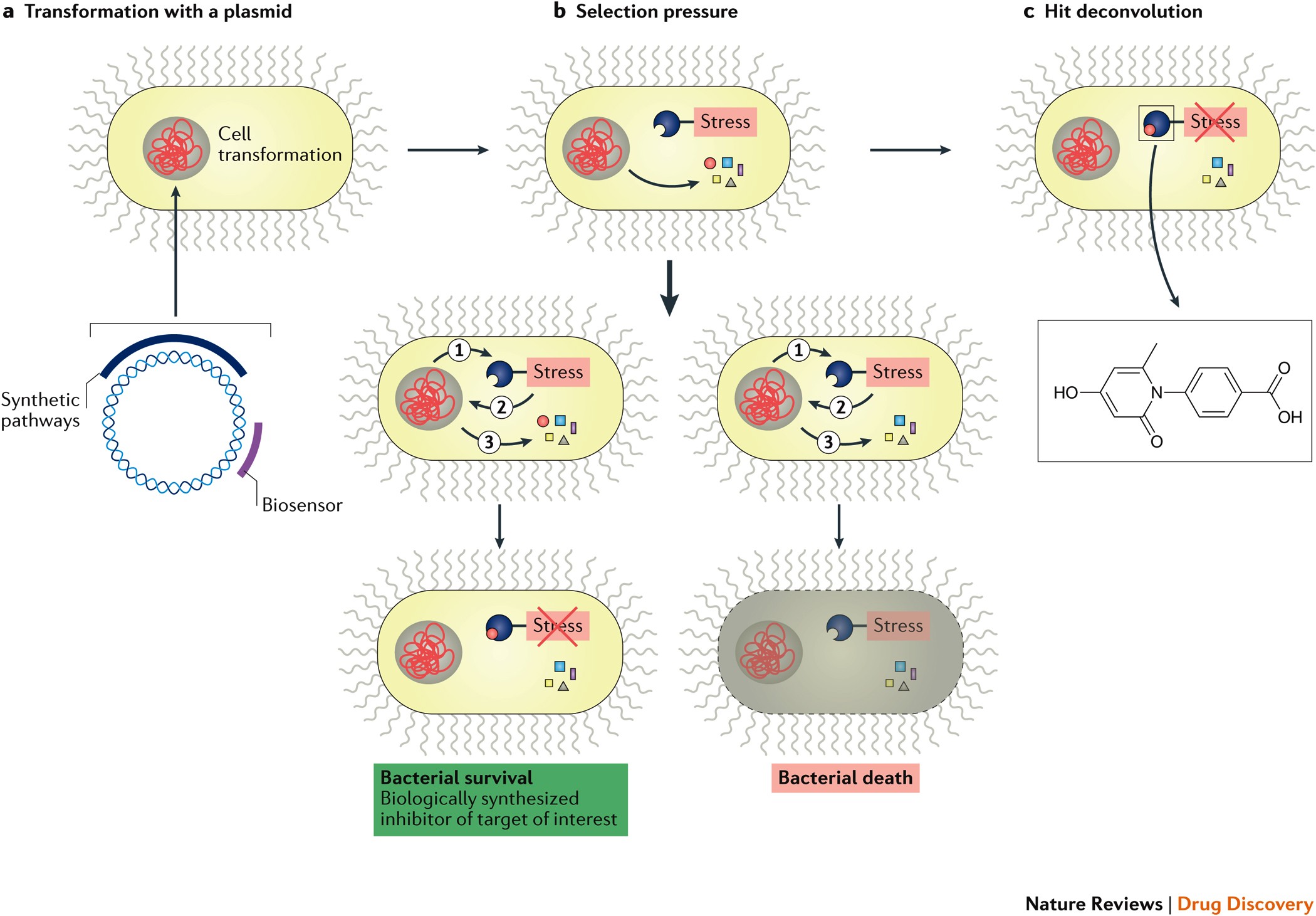
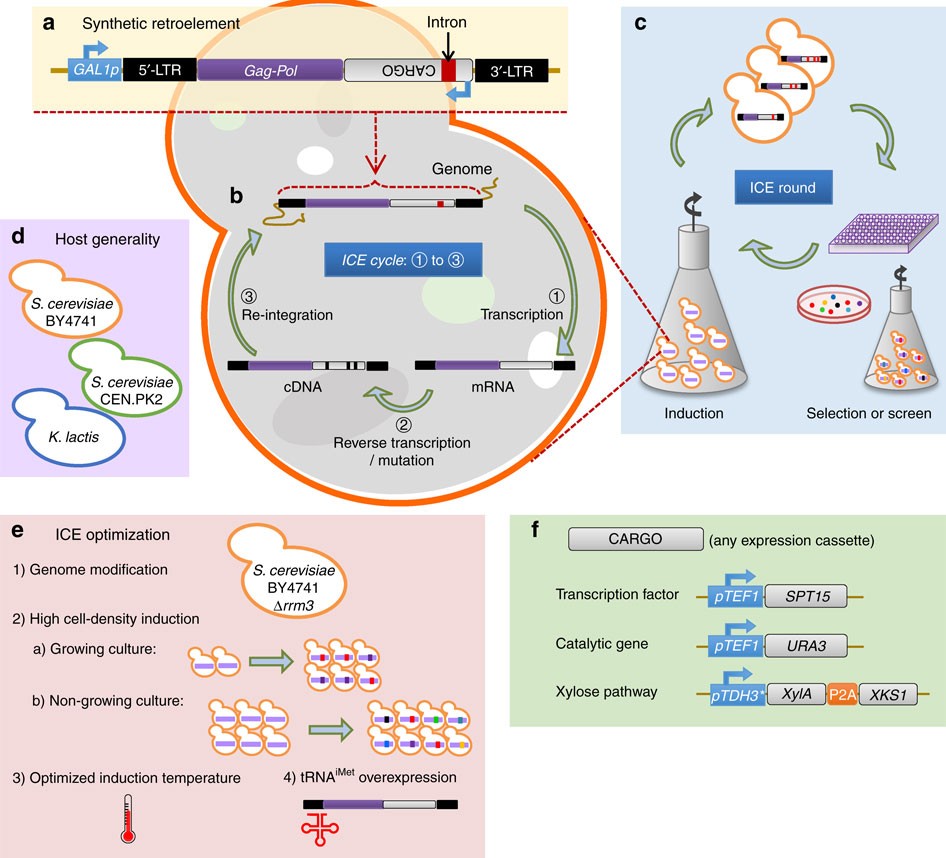
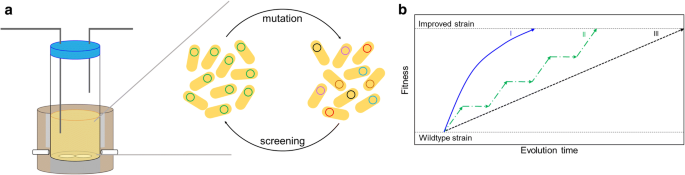
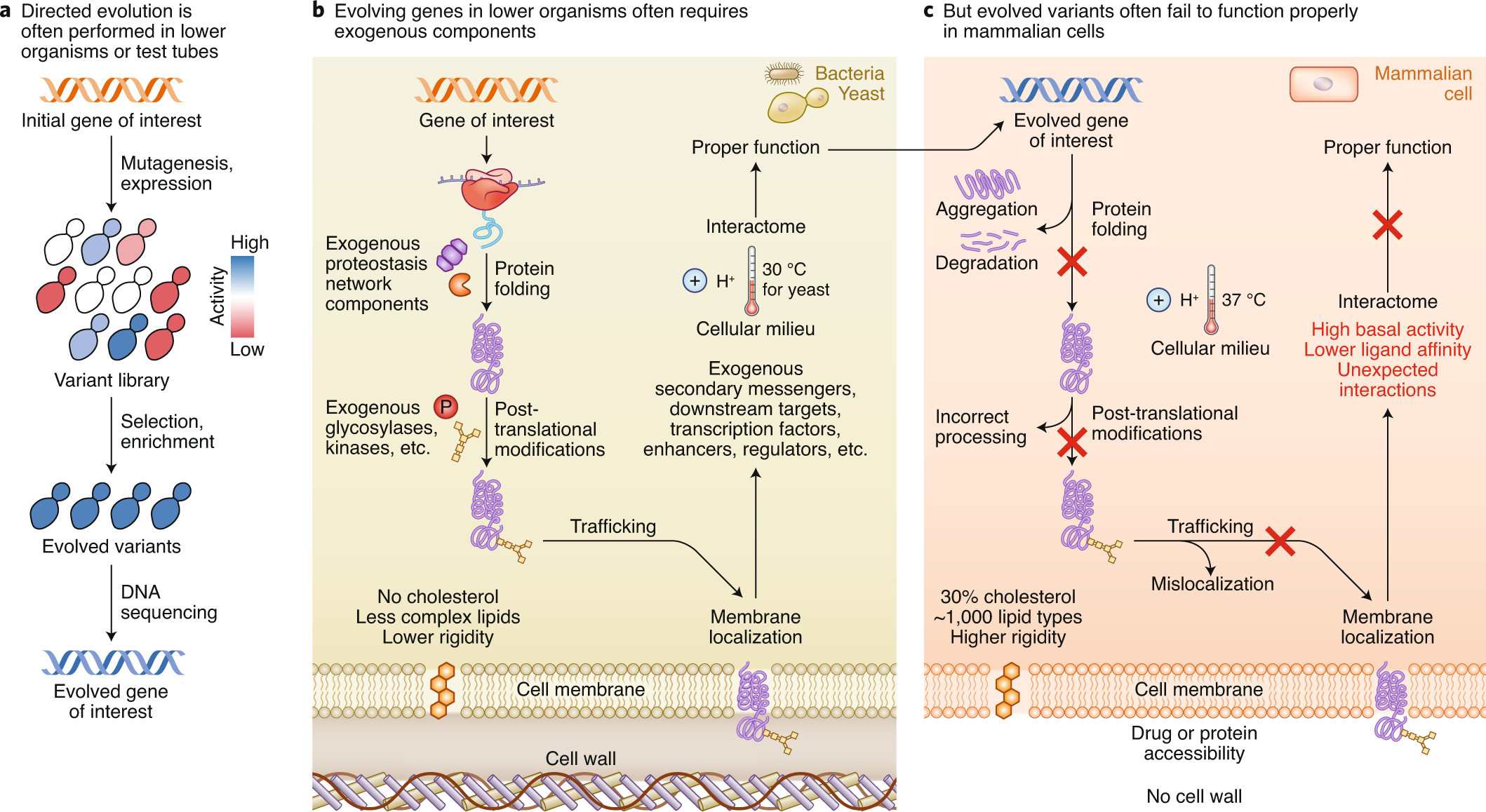
We present automated continuous evolution ACE a platform for the hands-free directed evolution of biomolecules. I The mutant library should be designed to contain sufficient genetic diversity to increase the probability of reaching a maximum peak in the fitness landscape 73. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli.
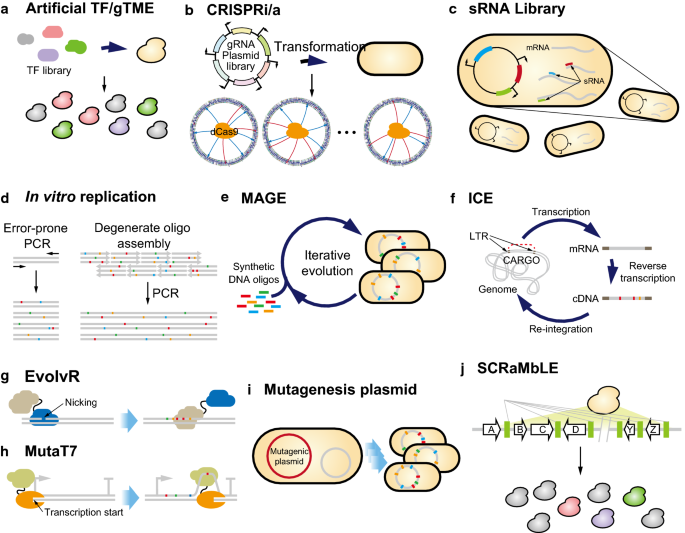
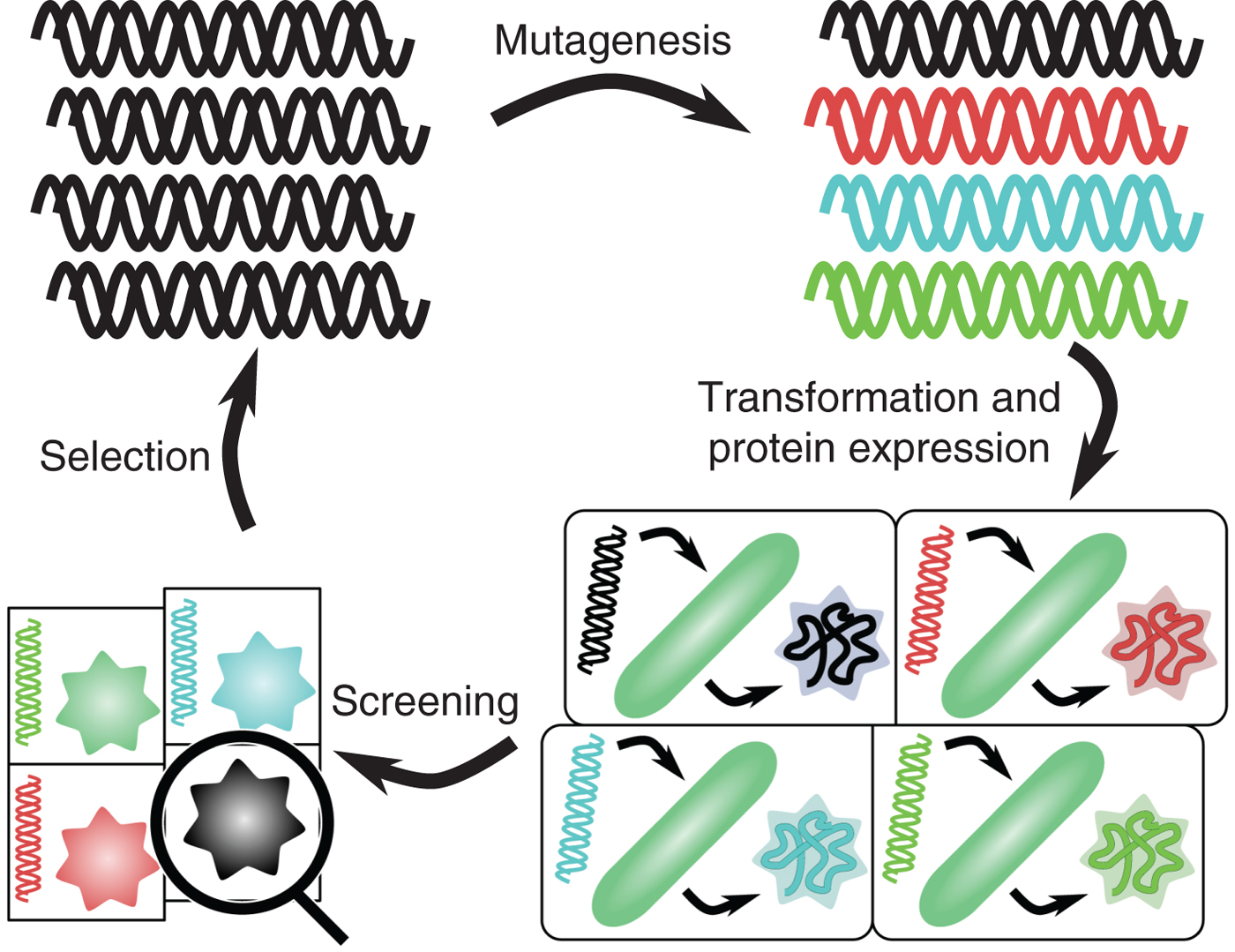
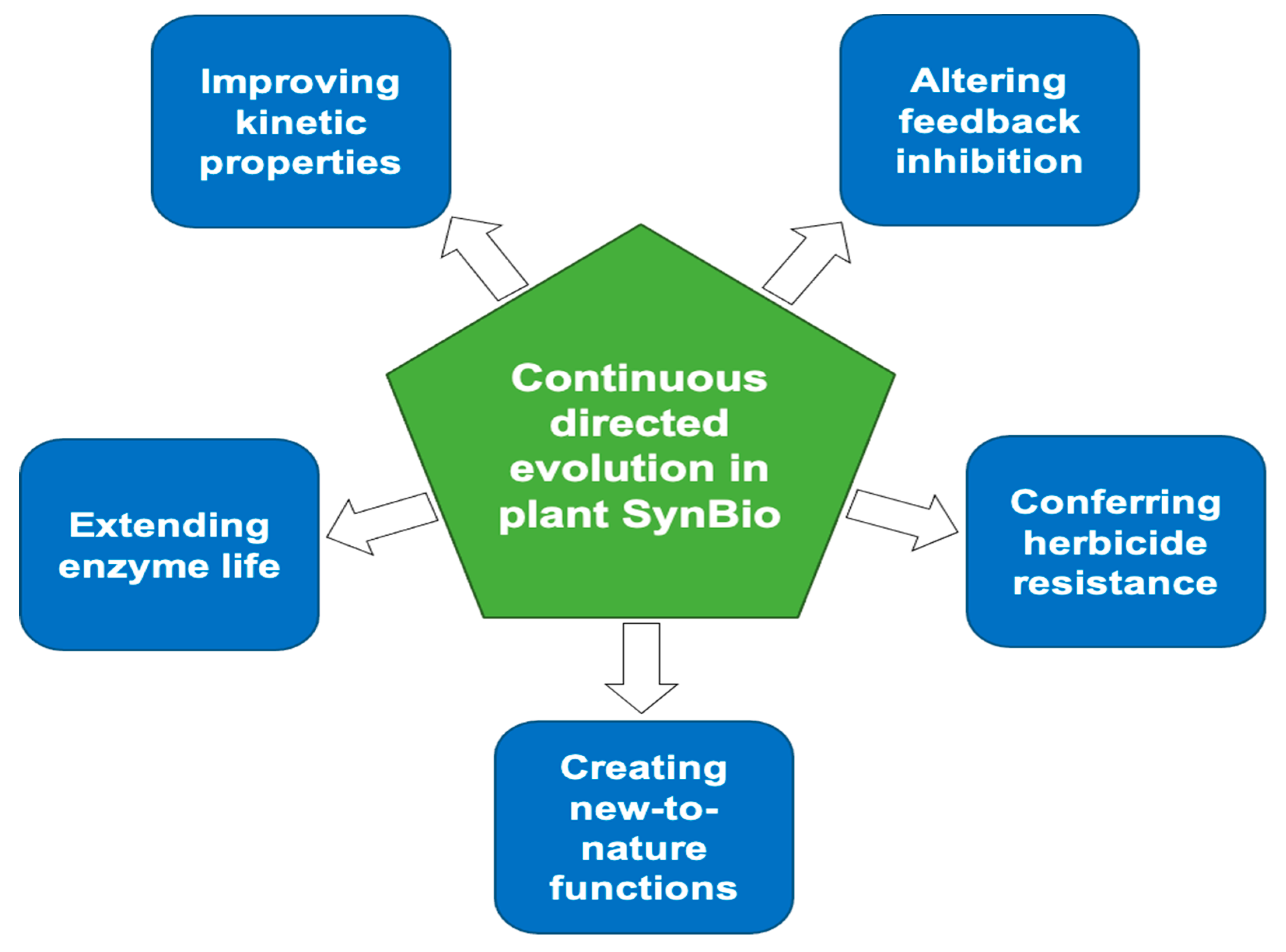
The uptake of directed evolution methods is increasing as these powerful systems can be utilized to develop new biomolecules with alterednovel activities for example proteins with new catalytic functions or substrate specificities and nucleic acids. ACE pairs OrthoRep a genetic system for continuous targeted mutagenesis of user-selected genes in vivo with eVOLVER a scalable and automated continuous culture device for precise multiparameter regulation of growth conditions.
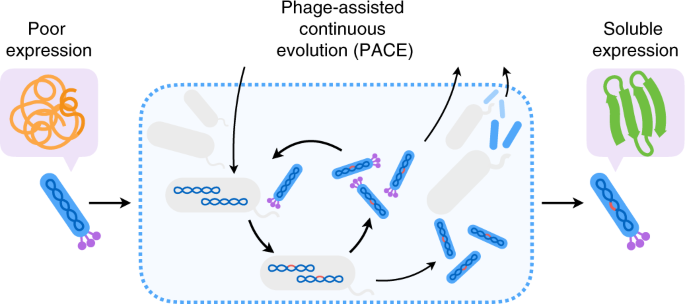
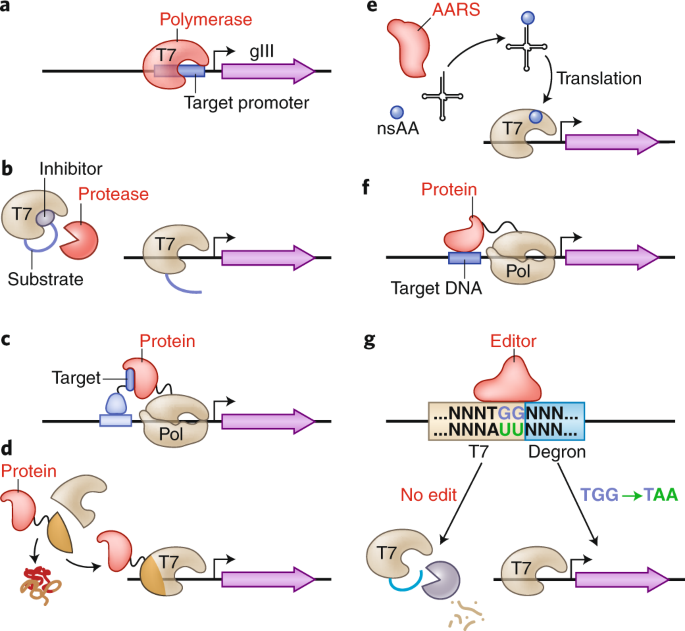
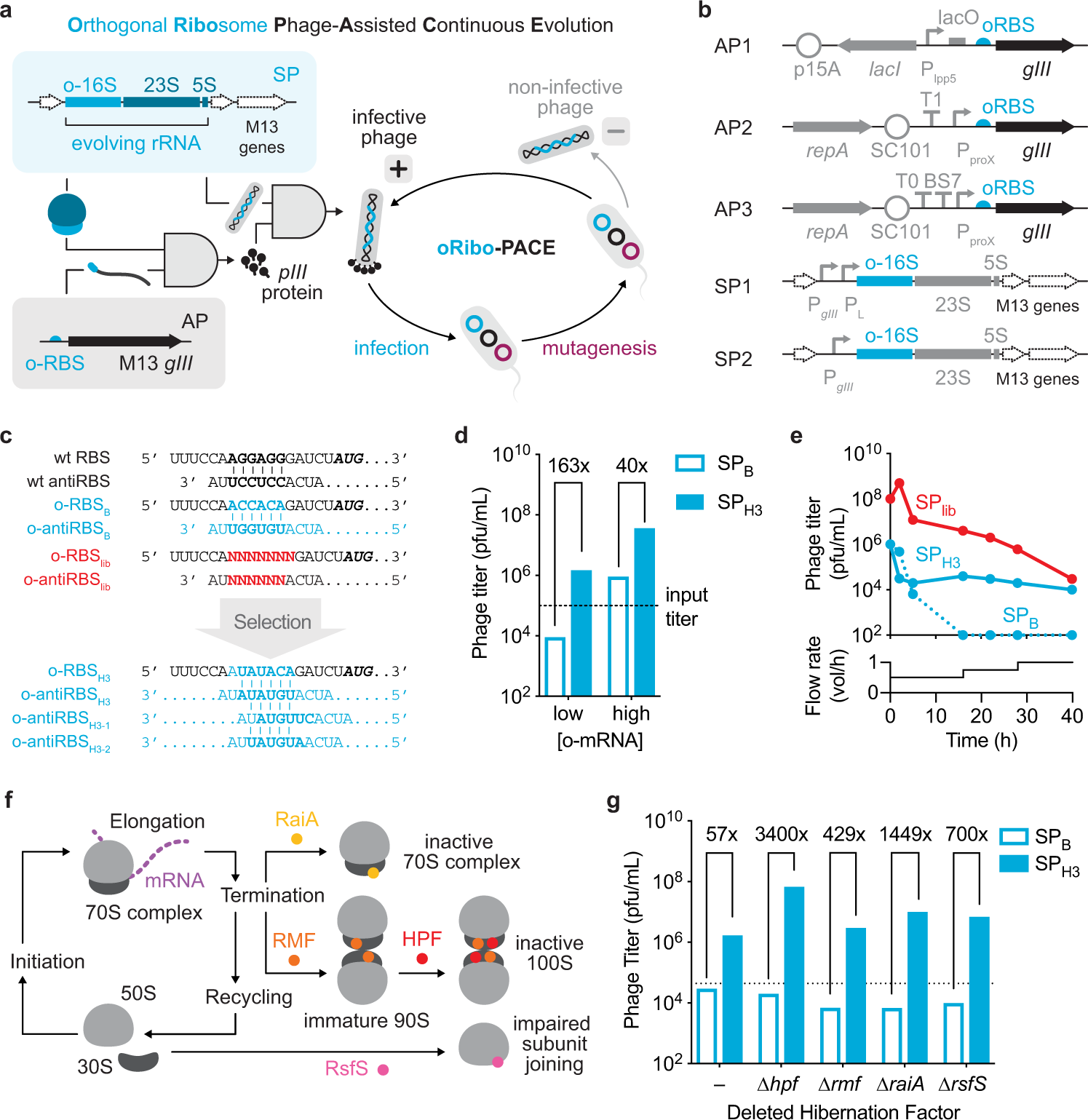
Phage-Assisted Continuous Evolution PACE.
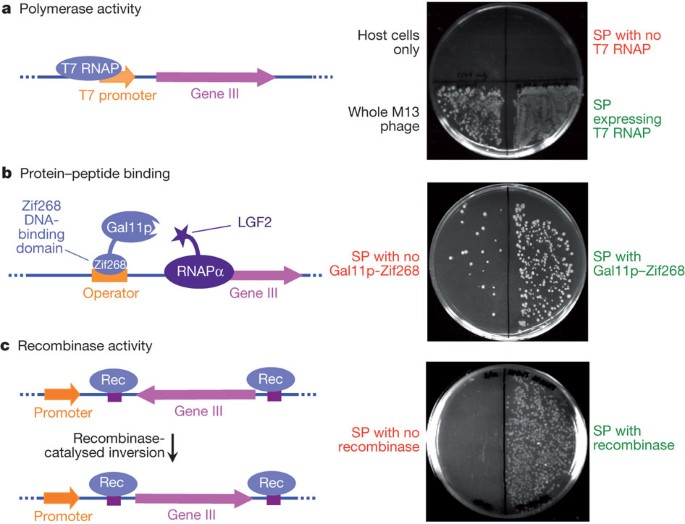
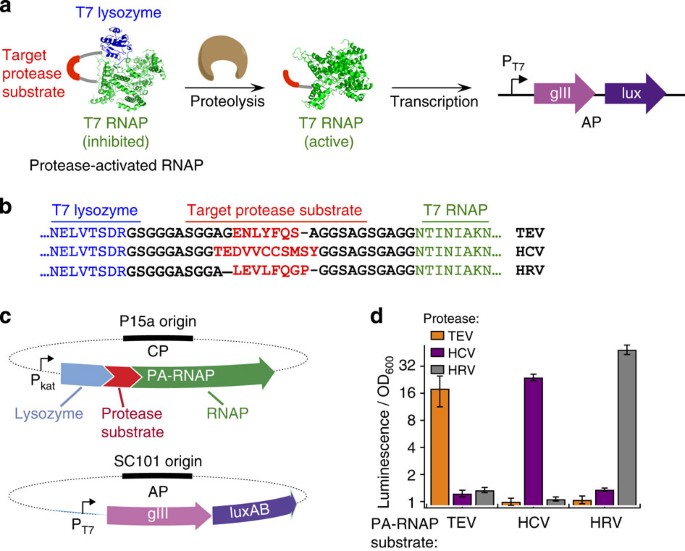
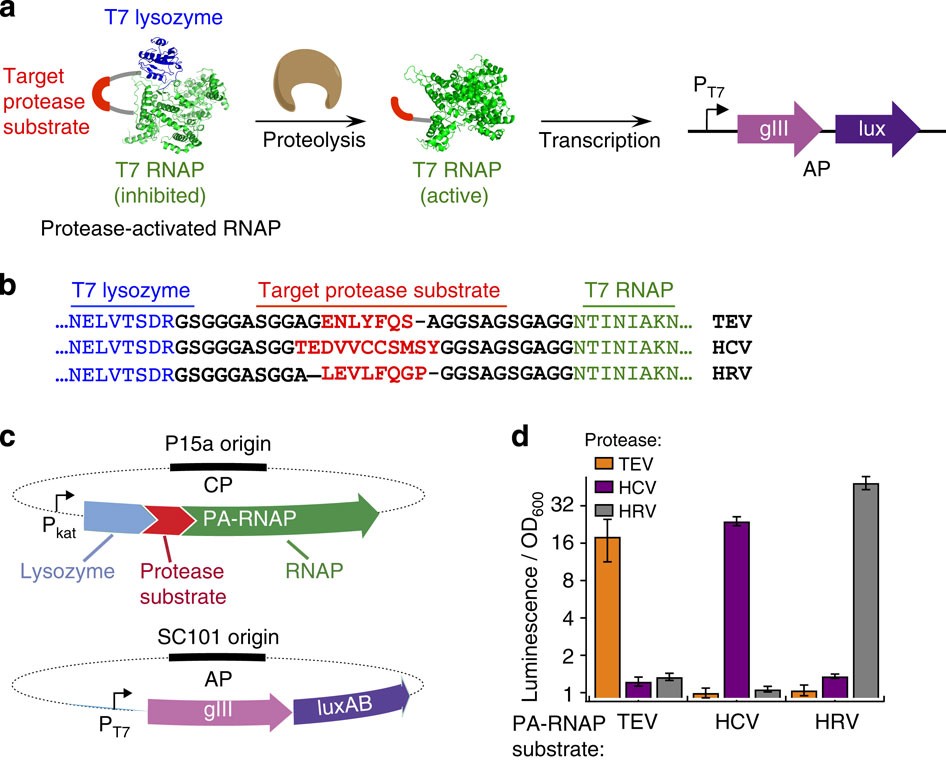
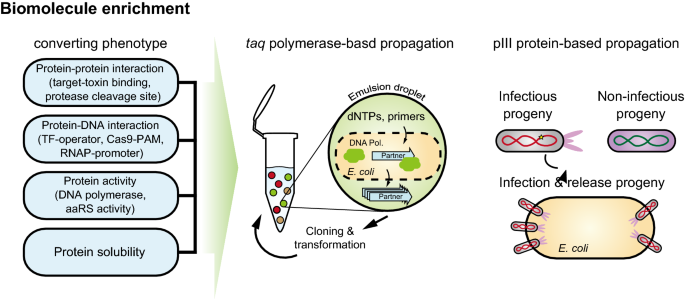
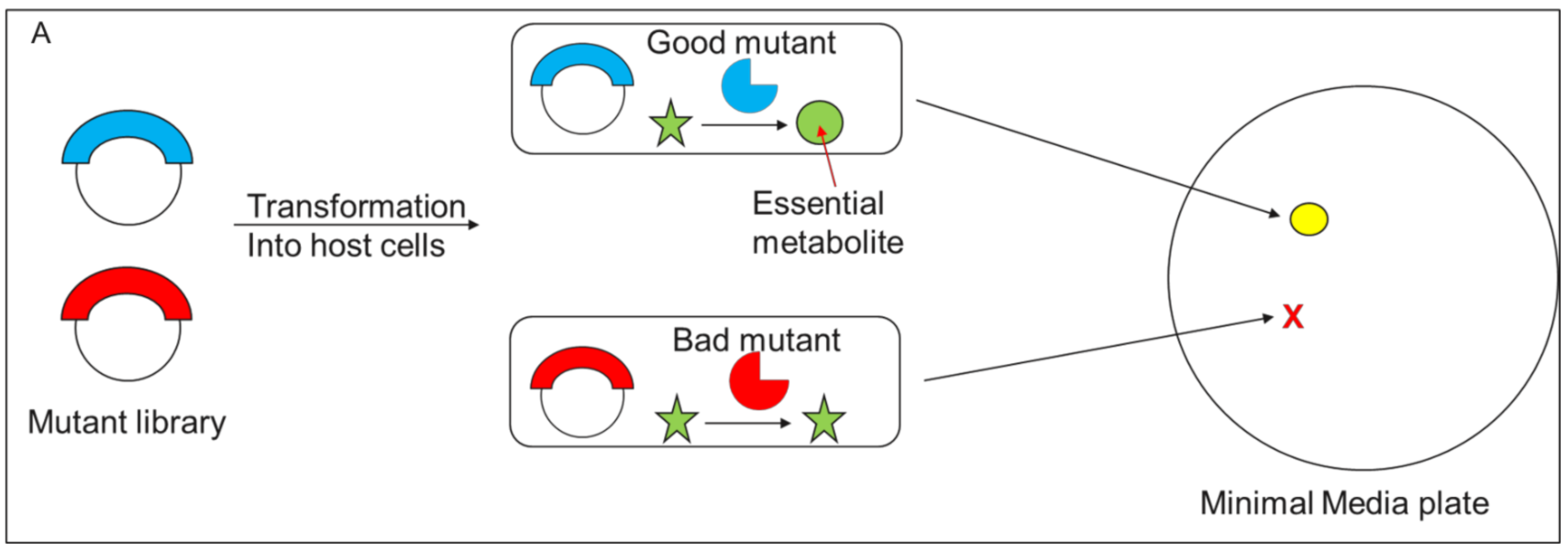
The uptake of directed evolution methods is increasing as these powerful systems can be utilized to develop new biomolecules with alterednovel activities for example proteins with new catalytic functions or substrate specificities and nucleic acids. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in E. Here we describe a system for the continuous directed evolution of proteases using phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE that links the proteolysis of a target peptide to phage propagation. To successfully evolve biomolecules genetic pathways or even genomes in a directed manner it is crucial that the evolution system meets three fundamental criteria. Phage-Assisted Continuous Evolution PACE. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of interest. A System for the Continuous Directed Evolution of Biomolecules articleEsvelt2011ASF titleA System for the Continuous Directed Evolution of Biomolecules authorK.
Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli. The uptake of directed evolution methods is increasing as these powerful systems can be utilized to develop new biomolecules with alterednovel activities for example proteins with new catalytic functions or substrate specificities and nucleic acids. Here we describe a system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be linked to protein production in Escherichia coli. Now describe a phage-assisted continuous evolution system that enables the continuous directed evolution of gene-encoded molecules that can be. Esvelt et al. During phage-assisted continuous evolution PACE evolving genes are transferred from host cell to host cell through a modified bacteriophage life cycle in a manner that is dependent on the activity of interest.





















Post a Comment for "A System For The Continuous Directed Evolution Of Biomolecules"